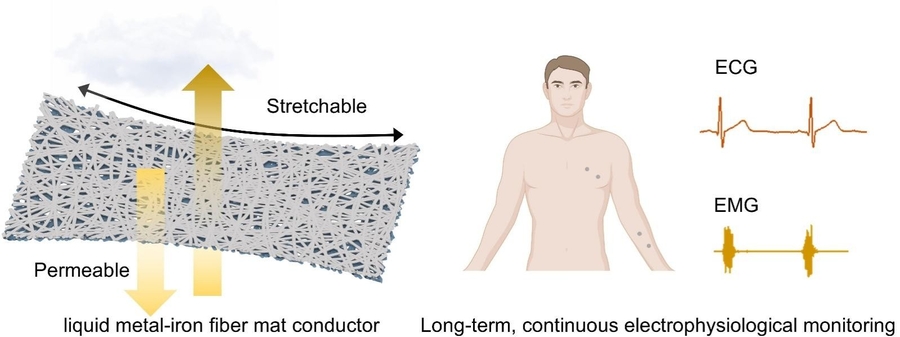
Highly elastic, permeable liquid metal–iron fibre mat conductor for electrophysiological monitoring
KNOXVILLE, TN, March 04, 2025 /24-7PressRelease/ — In a ground-breaking first, researchers have fabricated a highly elastic, permeable liquid metal–iron fiber mat conductor with exceptional stretchability, electrical conductivity, and recyclability, demonstrating its potential for long-term electrophysiological monitoring in healthcare applications.
With the rapid advancement of wearable technologies, the mechanical properties of stretchable electronics have greatly improved, driving the development of robust electronic interfaces for sensing and stimulation. This progress has expanded the range of applications, particularly in health monitoring, human-machine interfaces, and robotic prosthetics. However, despite these advancements, designing stretchable conductors that simultaneously offer high conductivity, stretchability, and long-term wearability remains a challenge.
In a study published in the KeAi journal Wearable Electronics, a group of researchers from China and Israel has designed a novel conductor-a highly elastic, permeable liquid metal-iron fiber mat conductor-capable of long-term, continuous, and high-fidelity electrophysiological monitoring.
“Liquid metal-based stretchable conductors have garnered much attention for their broad applications in bioelectronics, wearable devices and soft robotics,” explains one of the study’s authors, Yan Wang, a professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Guangdong Technion-Israel Institute of Technology. “However, their high surface tension and weak interfacial bonding with most elastomers complicate their seamless integration into flexible or stretchable devices. Furthermore, conventional liquid metal-based conductors often lack sufficient permeability, leading to poor moisture management and discomfort during prolonged wear.”
The team found that by coating a mixture of liquid metal and iron powder onto fiber mats, conductors with exceptional stretchability, high conductivity, and outstanding electromechanical stability were achieved.
“These conductors are capable of long-term, continuous, high-fidelity electrophysiological monitoring, highlighting their potential applications in early disease detection, bioelectronics, and wearable health monitoring systems,” adds Wang.
Until now, the recyclability of liquid metals has remained limited, and the combination of complex fabrication processes and suboptimal breathability has posed significant challenges for their practical application in epidermal electronic devices.
“Our newly proposed approach demonstrates that high-performance conductors can be achieved through a simple fabrication process while maintaining full recyclability,” says Wang. “We hope that our findings provide a new perspective for the development of stretchable conductors with high conductivity, biocompatibility, breathability, and recyclability to contribute to the development of novel wearable health monitoring technologies and other bioelectronic devices.”
References
DOI
10.1016/j.wees.2024.12.006
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wees.2024.12.006
Funding information
This research was supported fr the Natural Science Foundation of China (grant No.: 52303371), Guangdong Science and Technology Department (grant No.: 2021B0301030005, STKJ2023075, 2022A1515110209), Guangdong Education Department (grant No.: 2022KQNCX112), Seed Fund (GCII-Seed-202406) from GTIIT Changzhou Innovation Institute, and the Key Discipline (KD) Fund, the Technion, and the Start-Up Fund from Guangdong Technion.
About Wearable Electronics
Wearable Electronics is a peer-reviewed open access journal covering all aspects of wearable electronics. The journal invites the submission of research papers, reviews, and rapid communications, aiming to present innovative directions for further research and technological advancements in this significant field. It encompasses both applied and fundamental aspects, including wearable electronic materials, wearable electronic devices, and manufacturing technologies of such devices. By incorporating the expertise of scientists, engineers, and industry professionals, the journal strives to address the pivotal challenges that shape the field of wearable science and its core technologies.
Contact
Yan Wang
yan.wang@gtiit.edu.cn
Chuanlink Innovations, where revolutionary ideas meet their true potential. Our name, rooted in the essence of transmission and connection, reflects our commitment to fostering innovation and facilitating the journey of ideas from inception to realization.
Related Link:
http://chuanlink-innovations.com
—
For the original version of this press release, please visit 24-7PressRelease.com here